Securing the Employee Lifecycle: The Ultimate ISMS-Driven Approach Across ISO 27001:2022, NIS2, DORA, and GDPR
How One Missed Offboarding Sparked a Crisis: The CISO’s Wake-Up Call
Monday morning, and Sarah, CISO at a fast-growing FinTech, was jolted by a flagged alert, an attempted data exfiltration from a development server, using credentials belonging to Alex, a developer who’d resigned just days earlier. The handover was perfunctory: a rushed email, a quick goodbye, but nowhere in HR or IT were there records confirming Alex’s access was fully revoked. Had he just grabbed personal code, or was this industrial espionage?
The ensuing scramble to contain the incident uncovered uncomfortable answers. Alex’s minimal background check at hiring was a checkbox formality. His contract glossed over security obligations. And his departure process? A dusty checklist, never truly connected to real-time systems. Auditors, internal and soon external, wanted explanations. Regulators might not be far behind.
This wasn’t just about Alex. It exposed a universal, deeply consequential risk: the employee lifecycle as a threat surface. For every CISO and compliance manager, the challenge is clear: How do you assure airtight security from hire to retire, across every step, and stand ready to prove it under audit?
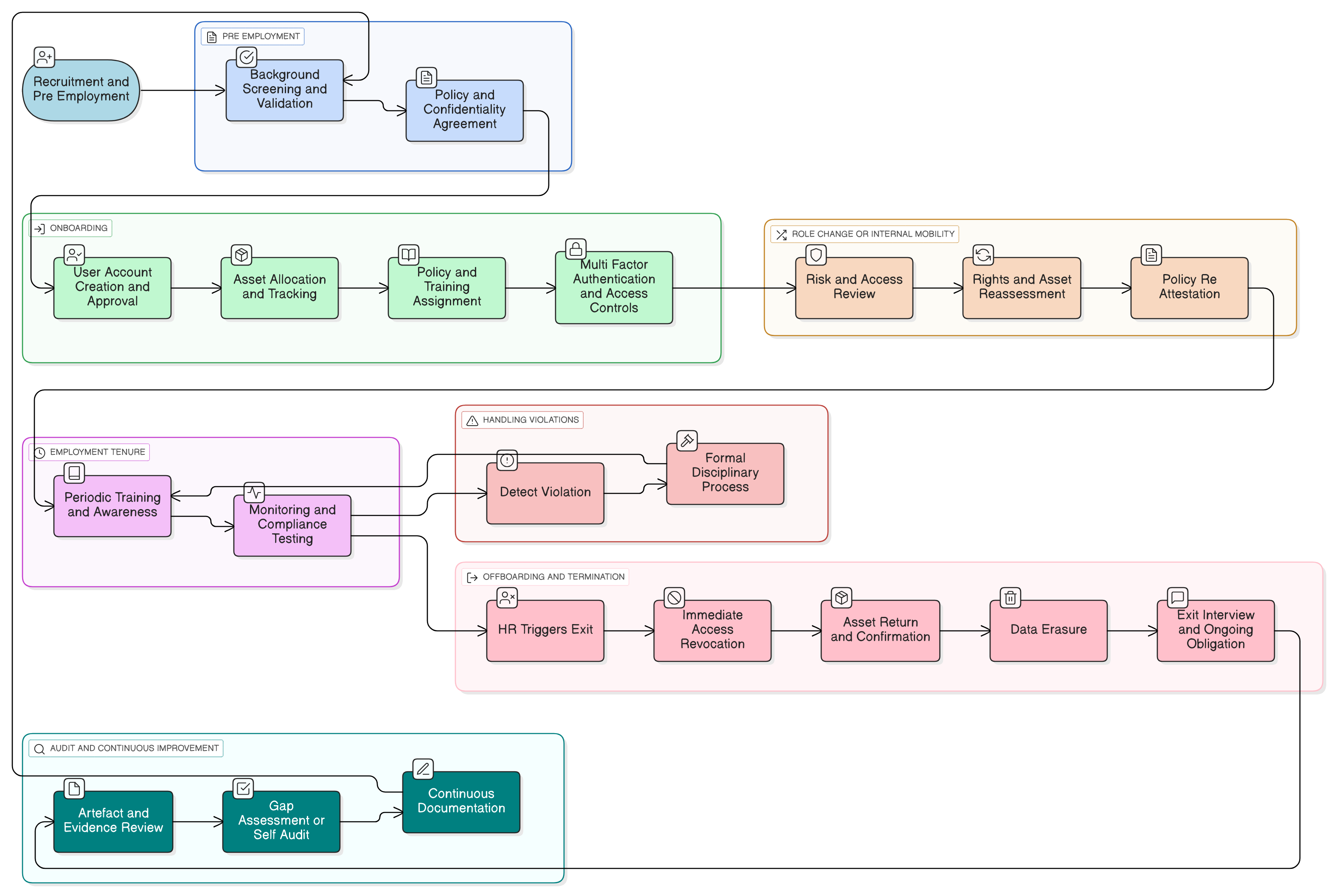
Why the Employee Lifecycle Is Now Your Security Perimeter
Modern enterprises face a complex regulatory gauntlet, ISO/IEC 27001:2022, NIS2, DORA, GDPR, NIST SP 800-53, and COBIT, just to name a few. The convergence point? Your people. Every phase, recruitment, onboarding, tenure, role change, exit, creates discrete, auditable risks for information security and data protection.
As articulated in Zenith Controls: The Cross-Compliance Guide:
“The employee lifecycle demands formal, auditable ties between HR, IT, and compliance. Each control must enforce identification, asset allocation, policy affirmation, and timely access management, with cross-mapping to major global standards.”
Let’s break down every lifecycle phase with detailed, actionable steps, controls, and real audit insight, leveraging Clarysec’s Zenith Blueprint, Zenith Controls, and policy templates.
1. Recruitment & Pre-Employment: Establishing Trust Before Day One
A secure workforce begins long before the first salary payment. Superficial screening is no longer enough; proportional, risk-based verification is required by both standards and regulators.
Key Controls & Policy Mapping
| Control (ISO/IEC 27001:2022) | Zenith Controls Attribute | Related Standards | Cross-Regulatory Mapping |
|---|---|---|---|
| A.6.1 Human resource security | Identification/Screening | ISO/IEC 27701:2019 7.2.1 | GDPR Article 32: Security of Processing |
| A.5.1 Policies for HR | Responsibility | ISO/IEC 37301:2021 | NIST SP 800-53: PL-4, AC-2 |
| 6.1.1 Screening | Preventive Control | ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | NIS2, DORA workforce due diligence |
5.1 Onboarding Process 5.1.1 Onboarding of new hires, contractors, or third-party users must follow a structured process that includes: 5.1.1.1 Background verification (where legally permitted) Onboarding and Termination Policy, Clause 5.1(Onboarding and Termination Policy)
Action Steps with Clarysec
- Deploy background screening proportional to business risk, validated via documented evidence before contract finalization.
- Require digital policy acknowledgment and confidentiality agreement attestation.
Mapped in Zenith Blueprint: Auditor’s 30-Step Roadmap, Phase 1 (“Scope and Context”), Phase 3 (“Human Resource Security”), Step 9: “Formal verification procedures for new hires.”
2. Onboarding: Mapping Access to Role, Recording Every Asset
Onboarding is the main inflection point for risk introduction. Poorly governed account provisioning and unclear asset ownership create the perfect conditions for data leaks, sometimes years later.
Controls & Implementation
| Control | Zenith Attribute | Other Standards | Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| A.7.1 User access mgmt | Provisioning, Authentication | ISO/IEC 27017:2021 | Access assignment record |
| A.7.2 User responsibilities | Policy Awareness | ISO/IEC 27701:2019 | Asset allocation registry |
| 6.2 Terms of employment | Contractual awareness | ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | Signed contract, NDA |
“All hardware and software assets allocated to personnel shall be recorded, tracked, and regularly reviewed for compliance with the Asset Management Policy.”
Asset management policy, Section 5.2 (Asset management policy)
Best Practices with Clarysec
- Launch onboarding workflow capturing:
- User account creation with approval record
- Asset allocations (hardware, software, IDs) linked to personnel profile
- Multi-factor authentication and secrets management
- Role-based policy and training requirements
- Attach all records to user and role, mapped in Zenith Blueprint, Step 12: Identity and Access Assignment.
3. Role Change: Navigating Risk in Internal Mobility
Internal promotions, transfers, and functional shifts are a major driver of “access creep.” Without rigorous process, privileged rights and asset sprawl undermine even the most mature security programs.
Controls & Audit Table
| Audit Standard | What’s Needed for Audit | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | Revised access logs, asset updates | Policy re-attestation, access change record |
| NIST SP 800-53 | Technical enforcement of least privilege | Separation of duties, approval workflow |
| COBIT 2019 APO07 | Role-transition documentation | Asset and rights lifecycle |
“Whenever an employee’s role or departmental affiliation changes, their access rights and asset assignments must be formally reassessed and updated, with obsolete access withdrawn.”
Access control policy, Section 6.4 (Access control policy)
Implementation Using Clarysec
- HR triggers risk assessment and access review upon any internal movement.
- IT and management jointly approve or revoke privileges; all changes are logged and linked back to user’s compliance profile.
- Zenith Controls highlights this under A.7.2 (“User responsibilities”) and A.8.2 (“Change of employment”).
- Every update is evidence for future audit.
4. Employment Tenure: Maintaining a Living Human Firewall
The longest and most critical risk window is ongoing employment. Without meaningful awareness, monitoring, and rigorous response, the organization’s “human firewall” will inevitably fail.
Awareness, Monitoring & Enforcement
| Control | Attribute | Linked Standards | Key Audit Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| A.7.3 User monitoring | Continuous compliance | ISO/IEC 27032:2021 | Is there proactive detection? |
| 6.3 Awareness | Training & Testing | GDPR/NIS2 (Art 21) | Are records and evidence collected? |
“All personnel shall participate in annual security training, with completion records maintained by HR and monitored by the compliance office.”
Information security awareness and training policy, Section 7.2 (Information Security Awareness and Training Policy)
How Clarysec Tightens the Process
- Mandate annual (or more frequent) security awareness and role-based training, tracked in an LMS integrated with access management.
- Launch simulated phishing exercises and measure response; map results to individual employee profile for ongoing improvements.
- Use Zenith Blueprint, Step 19: Awareness Training for continuous improvement.
5. Handling Violations: Enforcing the Disciplinary Process
No lifecycle management is complete without a clear, enforced and auditable escalation route for breaches of policy and responsibility.
Control and Policy
| Control | Attribute | Policy Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 6.4 Disciplinary Process | Accountability | HR/Compliance escalation docs |
- Develop and document a formal, coordinated approach with HR and legal
- Clearly communicate policy and escalation mechanisms as required by Zenith Controls and COBIT APO07
6. Offboarding & Termination: Closing Access Gaps Fast
The “goodbye” phase is often where CISO nightmares, like Sarah’s, are born. Account lingering, forgotten assets, and inadequate documentation become rich targets for insiders and external attackers, especially during times of organizational stress or staff churn.
Control Mapping and Protocol
| Step | Zenith Blueprint Reference | Artefact Required |
|---|---|---|
| HR notifies IT of exit | Step 24 | Ticket record |
| Immediate access revocation | Step 25 | Access log |
| Asset return and confirmation | Step 25 | Asset intake sheet |
| Erasure of company data | Step 26 | Data purge report |
| Document exit interview | Step 27 | Interview notes |
Policy Quotable:
5.3 Termination Process
5.3.1 Upon notification of a voluntary or involuntary departure, HR shall:
5.3.1.1 Communicate the effective date and status to IT, Facilities, and Security
5.3.1.2 Trigger deprovisioning, asset collection, and revocation workflows
5.3.1.3 Ensure the terminated user is removed from distribution lists, communications systems, and remote access platforms
5.3.1.4 Immediate access revocation (within 4 business hours) is required for high-privilege or high-risk users (e.g., administrators, finance staff).
5.4 Access Revocation and Asset Recovery…."
Onboarding and Termination Policy, Clause 5.1(Onboarding and Termination Policy)
Mapped Frameworks, Why Offboarding Is a Compliance Crossroads
| Framework | Key Clause/Control | How Offboarding Maps |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Article 32 (Security), 17 (Erasure) | Timely access removal & data deletion |
| DORA | Article 9 (ICT risk) | Onboarding/offboarding staff risks |
| NIST CSF | PR.AC-4 | All accounts revoked, no lingering rights |
| COBIT 2019 | APO07.03 | Workforce exit process & documentation |
| ISACA | Asset and access lifecycle | Policy to records alignment |
As summarized in Zenith Controls: “Offboarding requires documented, real-time evidence of access revocation, asset return, and data erasure, mapped for multi-framework compliance.”
7. Advanced Cross-Compliance: Satisfying NIS2, DORA, GDPR, NIST, COBIT, and More
The employee lifecycle is now at the intersection of global, sectoral, and national regimes.
Unified Controls, One Lifecycle Protocol
- NIS2 (Art. 21): Enforces HR security, annual awareness, offboarding validation.
- DORA: Demands asset inventory, risk reporting, third-party role tracking.
- GDPR: Data minimization, “right to erasure”, employment record discipline.
- NIST SP 800-53: Tightens privileged access, monitoring, separation of duties.
- COBIT 2019: Requires asset, access, and policy lifecycle traceability.
Only a structured, crosswalked protocol like that enabled by Zenith Controls and the Zenith Blueprint guarantees full-spectrum coverage and audit readiness.
Audit Realities: What Every Auditor Seeks in Lifecycle Security
Auditors approach lifecycle security through different, but overlapping, lenses:
| Auditor Type | Focus Area | Requested Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001 | Process, policy, consistency | Policy docs, onboarding/offboarding logs, checklists |
| NIST | Control effectiveness | System/access logs, technical artefacts |
| COBIT/ISACA | Governance, monitoring | Change mgmt docs, maturity metrics |
| GDPR Regulator | Data protection | Deletion records, privacy notices, HR files |
Quote from Zenith Controls:
“Effective security lies in how quickly organizations can prove compliant lifecycle management under scrutiny.” (Zenith Controls)
Pitfalls and Best Practices: Frontline Lessons Learned
Pitfalls
- Disconnected HR and IT accountability
- Onboarding not mapped to risks, documented incompletely
- Forgotten accounts/assets after departure or promotion
- Missing evidence for screening or training
- Manual, non-repeatable checklist processes
Best Practices with Clarysec
- Use Zenith Blueprint to guide and document each step of the lifecycle, mapping to controls and artefacts.
- Deploy Zenith Controls to bridge ISO/IEC 27001:2022, NIS2, DORA, GDPR, NIST, COBIT, and more with a single framework.
- Automate evidence collection and cross-linking between IT, HR, and compliance.
- Schedule regular, role-tailored training and simulate real-world threats.
- Run pre-audit self-assessments using Clarysec templates, closing gaps before auditors arrive.
Clarysec in Action: A Realistic Framework for Multi-Jurisdiction, Multi-Standard Success
Let’s envision a multinational insurer leveraging the Clarysec ecosystem:
- Recruitment launches with risk-based background checks, digitally evidenced.
- Onboarding triggers IT and HR provisioning, assets and training mapped to employee ID.
- Role changes spark a dynamic workflow, rights and assets review, risk updates.
- Training is tracked, completion enforced, non-compliance flagged for follow-up.
- Offboarding is a sequence: HR triggers, IT revokes, assets returned, data wiped, all confirmed by timed artefacts.
- Auditors access a unified artefact repository, with traceability across every standard.
This isn’t theory, it’s operational resilience, audit confidence, and compliance efficiency, powered by the Clarysec stack.
Next Steps: From Reactive Scrambling to Proactive Control
Sarah’s story is a stark warning: unchecked lifecycle risk is a security and compliance disaster waiting to happen. Organizations that embed these controls, map them holistically, and evidence every step move from perpetual audit panic to streamlined, strategic advantage.
Take action today:
- Book a personalized consultation to align Zenith Blueprint and Controls with your unique HR and IT landscape.
- Run a self-audit simulation to expose and resolve lifecycle gaps, before your next surprise resignation or regulator call.
Clarysec: Secure every stage, prove every step, withstand every audit.
References:
Frequently Asked Questions
About the Author

Igor Petreski
Compliance Systems Architect, Clarysec LLC
Igor Petreski is a cybersecurity leader with over 30 years of experience in information technology and a dedicated decade specializing in global Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC).Core Credentials & Qualifications:• MSc in Cyber Security from Royal Holloway, University of London• PECB-Certified ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor & Trainer• Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) from ISACA• Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) from ISACA • Certified Ethical Hacker from EC-Council